- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
How Does a Wired Water Meter Improve Water Management Efficiency?
2025-12-12
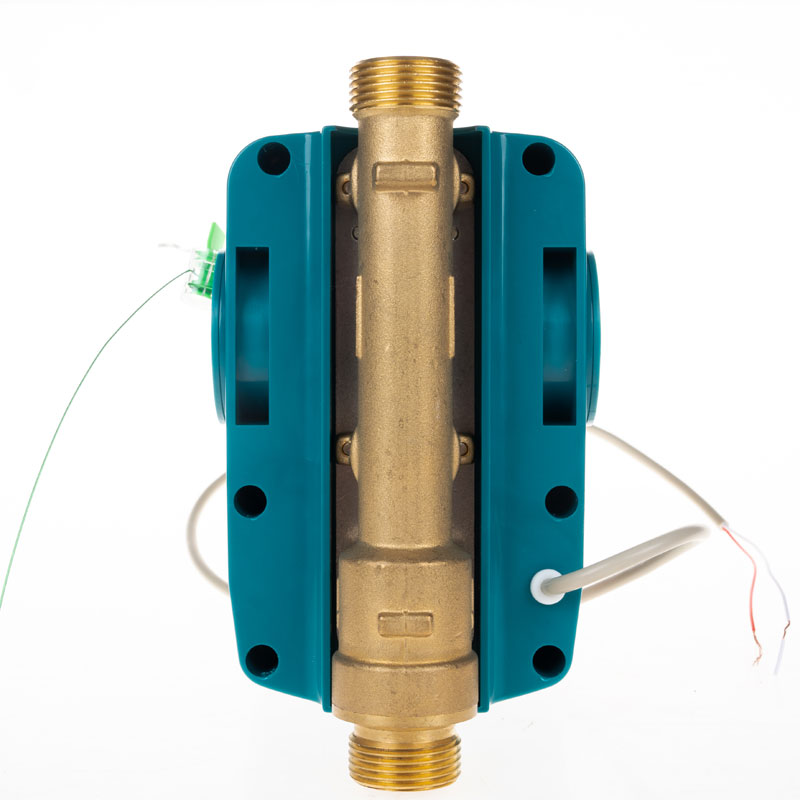
Wired water meters are precision devices designed to monitor and record water consumption with high accuracy. Unlike traditional mechanical meters, these instruments utilize advanced sensing technologies to transmit consumption data in real-time through wired connections. Wired water meters are increasingly critical for municipal water systems, industrial facilities, and residential complexes that aim to optimize water usage, reduce wastage, and improve billing accuracy.
Key Specifications of Wired Water Meters
To understand the capabilities of wired water meters, it is essential to review the core technical specifications. The following table provides a detailed overview of common parameters for high-performance wired water meters:
| Parameter | Specification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Volumetric / Ultrasonic / Electromagnetic | Determines the method of water flow measurement |
| Accuracy Class | ±1% to ±2% | Indicates precision level in recording water usage |
| Diameter Range | DN15–DN50 | Pipe size compatibility |
| Communication Interface | RS485, Modbus RTU | Standard wired communication protocols |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 50°C | Temperature range for reliable meter operation |
| Flow Rate Range | Qmin: 1 m³/h, Qmax: 30 m³/h | Minimum and maximum flow rates measurable |
| Power Supply | 12V–24V DC | Typical voltage requirements for continuous operation |
| Data Storage | Internal memory up to 36 months | Capacity for historical consumption data |
| Material | Brass / Stainless steel | Ensures durability and corrosion resistance |
| Protection Rating | IP65–IP68 | Dust and water ingress protection |
These specifications highlight the robustness, accuracy, and adaptability of wired water meters, making them suitable for a wide range of water management scenarios.
How Does a Wired Water Meter Operate in Different Environments?
Wired water meters function through sensors that detect the volumetric flow of water and convert this physical information into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted via wired connections to a central monitoring system, enabling real-time analysis and billing. The wired connection ensures stable data transmission over long distances, which is critical for municipal water networks where wireless signals may be unreliable due to interference or environmental obstacles.
Key operational advantages include:
-
Continuous Monitoring: Wired water meters provide uninterrupted data collection, crucial for detecting leaks and irregular consumption patterns.
-
High Data Accuracy: The elimination of wireless transmission noise enhances measurement precision.
-
Integration Capability: Wired meters can easily connect to SCADA systems, automated billing software, and energy management platforms.
Furthermore, these meters perform reliably in various environmental conditions, from residential pipelines to industrial water processing units. The choice of materials, such as stainless steel and brass, combined with IP-rated enclosures, ensures that the meters resist corrosion and maintain performance in wet, high-pressure, or chemically treated water systems.
How Can Wired Water Meters Contribute to Cost Reduction and Resource Management?
Water utilities and businesses face increasing pressure to optimize water usage and reduce operational costs. Wired water meters provide detailed and accurate consumption data, enabling several cost-saving and management benefits:
-
Leak Detection: Real-time monitoring identifies abnormal flow rates, allowing immediate corrective action.
-
Accurate Billing: Automated data collection minimizes human error, ensuring fair and precise billing for end-users.
-
Operational Efficiency: Continuous data logging supports predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and repair costs.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Detailed records of water usage facilitate compliance with municipal and environmental regulations.
By providing granular insights into water consumption patterns, wired water meters empower decision-makers to implement targeted water-saving initiatives, leading to significant cost reductions over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the lifespan of a wired water meter?
A1: Typically, wired water meters have a service life of 10–15 years, depending on the operating environment, water quality, and maintenance practices. Proper installation, regular calibration, and cleaning of the sensor components can extend operational longevity.
Q2: Can wired water meters handle high-pressure industrial applications?
A2: Yes, most industrial-grade wired water meters are designed to withstand pressures up to 1.6 MPa or higher. Materials such as stainless steel and brass, combined with robust housing, ensure the meter operates reliably in high-pressure environments while maintaining measurement accuracy.
How Are Wired Water Meters Evolving for Future Water Management Needs?
The evolution of wired water meters is closely linked to global trends in smart water management and digital infrastructure. Innovations are focused on enhancing connectivity, data granularity, and predictive analytics capabilities. Current developments include:
-
Advanced Sensor Technologies: Integration of ultrasonic and electromagnetic sensors provides higher accuracy for low and variable flow rates.
-
Edge Computing Capabilities: Some meters now include onboard processing to detect anomalies locally, reducing reliance on central systems.
-
Enhanced Data Security: Encrypted communication protocols protect sensitive consumption data from cyber threats.
-
Scalability: Modular designs allow easy expansion of monitoring networks in large residential or industrial complexes.
As water scarcity and efficiency demands intensify, wired water meters remain a critical component of sustainable water infrastructure, capable of supporting both current operational needs and future technological integrations.
How to Choose the Right Wired Water Meter for Your Needs?
Selecting an appropriate wired water meter requires careful evaluation of operational requirements, environmental conditions, and communication needs. Consider the following factors:
-
Flow Rate and Diameter Compatibility: Ensure the meter supports the expected minimum and maximum flow rates and matches the pipe dimensions.
-
Material and Durability: Choose materials that resist corrosion and are suitable for the water type being monitored.
-
Accuracy Class: Select a meter with a precision level appropriate for the billing or monitoring purpose.
-
Communication Interface: Verify that the meter’s wired protocol (e.g., RS485, Modbus RTU) aligns with existing network infrastructure.
-
Maintenance and Serviceability: Opt for meters with accessible calibration and maintenance options to ensure long-term accuracy and reliability.
Incorporating Xinkong wired water meters into water monitoring systems ensures industry-leading performance, robust durability, and seamless integration with existing infrastructure. Their products are designed to support both residential and industrial applications, offering detailed consumption monitoring, reduced water wastage, and enhanced operational efficiency. For more information on selecting the right solution and to request a customized quote, contact us today.